
The first of February marks the mid-point between the winter solstice and the spring equinox. It’s also known as Candlemas, the Christian festival of presenting Jesus at the temple. But long before Christianity, this time of year marked a more ancient celebration in Gaelic Britain: the rites of spring, and the fire festival of Imbolc.
Let’s get with the programme, Imbolc style, and parade down the street, and go pray for the health of the fields! It’s all about the soil. Modern soil scientists will agree.
February
The name February comes from the Latin ‘Februarius,’ referring to Februa; a Roman festival of ritual purification. Below, the Roman spa at Bath, UK.
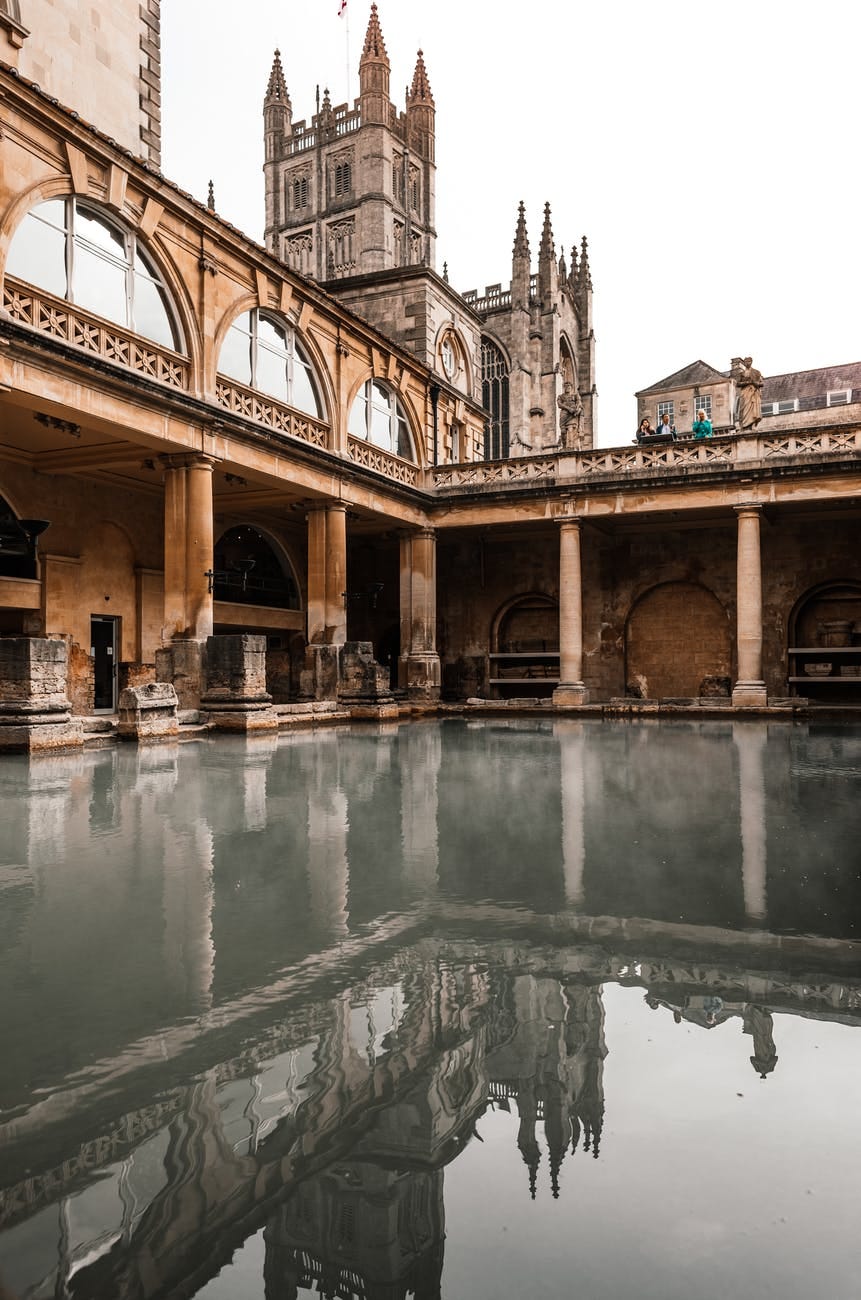

Two new months of January and February were added to the older Julian calendar in the 700’s BCE to create the new Gregorian calendar, matching it up more closely with the actual length of the Earth’s journey round the sun.
But the Anglo Saxons called February Sōlmōnath, from sōl , the Old English word for wet sand or mud, alluding to the weather this time of year, and the effects of rain and snow-melt. The romantic Solway Firth between North West England and South West Scotland is actually the massive tidal ‘Mud Way’ rather than the romantic ‘Sun Way.’

The northern English scholar monk , saint Bede, wrote that February was celebrated as “the month of cakes,” when ritual offerings of savory cakes and loaves of bread were made to ensure a good year’s harvest.
Imbolc
The fire festival of Imbolc and Brigid began as a neolithic festival marking the 1/2 way point between the winter solstice (Yule) and the spring equinox (Beltane.)
Imbolc marks the start of spring, celebrating the arrival of the goddess deity Brigid, “The Exalted One,” the harbinger of the first lambs, so vital to the survival of those early communities. The deity Brigid later became conflated with the Christian figure of Saint Brigid of Kildare.

‘Imbolc’ is thought to mean ‘in the belly,’ referring to the precious ewes in lamb. Soon it would -it will be- be the time of the first lambs, though the start of the lambing season can vary by up to two weeks in any given year.
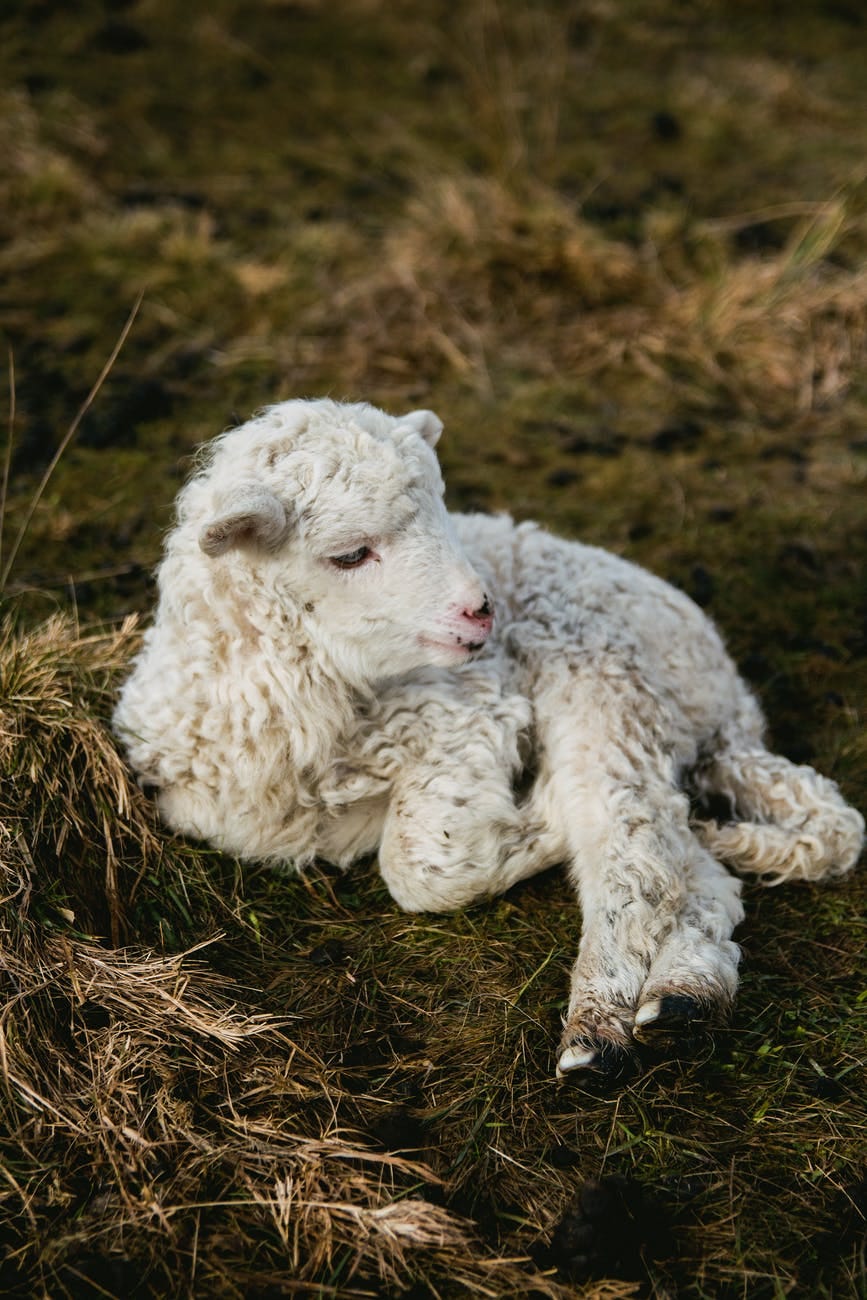

Brigid was a protector of women in childbirth, as well as the safe birthing of precious livestock. She was not only a goddess of the Tuatha Dé Danann, The Tribe of the Gods, but a triple goddess of healers, poets and smiths.

“The Tuatha de Danaan, the people of the (mother) goddess Danu in Celtic mythology; a race inhabiting Ireland before the arrival of the Milesians (the ancestors of the modern Irish). They were said to have been skilled in magic, and the earliest reference to them relates that, after they were banished from heaven because of their knowledge, they descended on Ireland in a cloud of mist. They were thought to have disappeared into the hills when overcome by the Milesians. The Leabhar Gabhála (Book of Invasions), a fictitious history of Ireland from the earliest times, treats them as actual people, and they were so regarded by native historians up to the 17th century. In popular legend they have become associated with the numerous fairies still supposed to inhabit the Irish landscape.”
From The Encylopedia Britannica
Brigid might visit one’s home at Imbolc. People would make a bed for her, and leave food and drink and items of clothing outside in the hope of receiving her blessings, petitioning her to protect their homes and livestock.
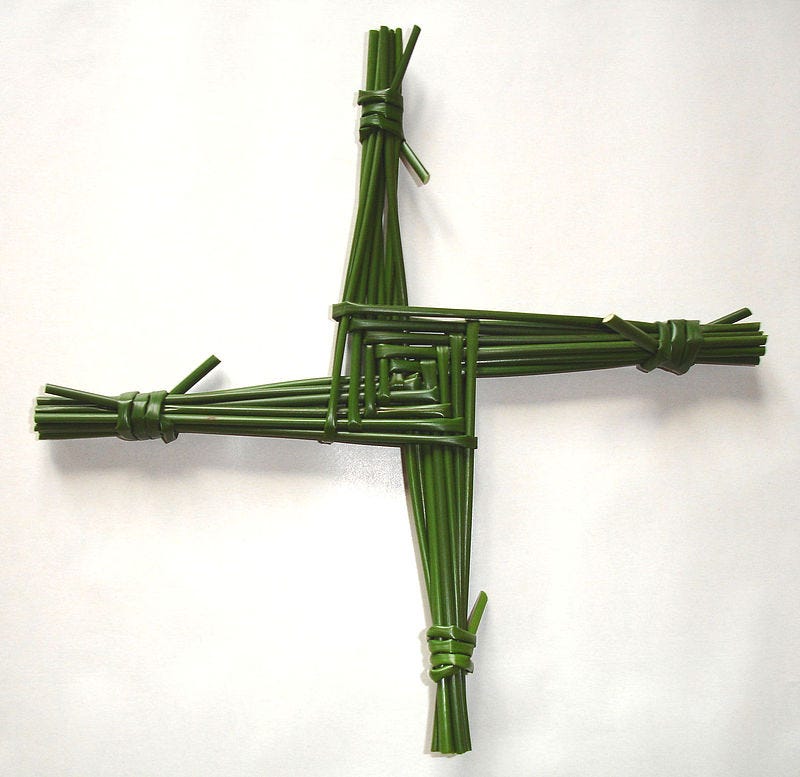
This was a time for feasting and visits to sacred wells, and a time for ritual divination. A St Brigid’s cross is made from rushes and was placed in doorways to protect the home from harm, representing the wheel of the seasons.

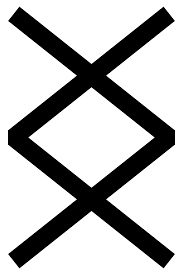
The Fire of Imbolc and the Fire Rune INGWAZ
Fire and Spring is not gentle. New life is not gentle. It rises up fast and fierce. It has to, or it would never break through. Spring is fierce in its quickening of new shoots. It is initiation. Spring is fire, just as Aries the Ram of the zodiac is a cardinal fire sign, though we do not enter Aries until late March.
Where Brigid represented an essentially feminine energy, the old Norse rune ING/INWAZ or INGUZ is a fire sign rune, associated with male fertility, vitality and recovery from sickness. You can read more about runes here in a previous blog post on my website, True Tarot Tales.
This ancient masculine fire rune represents the power and potential of “The Seed” matched with action. Literally, the name of this rune means “the seed of the god Ing.” When we say we are do-ing, writ-ing …anything at all with -ing at the end of it, we are describing an action, and indirectly, invoking the magical energy of Ingwaz.
The people would light bonfires on the hilltops by night, and by day, they might run cattle through the smoke of lower lying bonfires, asking divine protection for the livestock.
The Cailleach
Imbolc was a key moment in weather forecasting. This was the time when The Cailleach —the divine crone of Gaelic tradition—gathered firewood for the rest of the winter. If the Cailleach knew the winter was going to last a good while longer, she’d make sure of good weather during Imbolc and would use it to gather more firewood to top up her stores.
Bad weather at Imbolc was regarded as great news. It meant the Cailleach wasn’t worried about running out of firewood. She had turned over and gone back to sleep, and the worst of winter was almost over. We shall see. It has been cold and clear and glorious today where I live on the NW coast of England.

I am somewhat mixing up cultures, systems and traditions here, but Nature is the common ground and I make no apology for it. Imbolc falls in the second decan of the fixed Air sign of Aquarius. The fixed signs denote the height of a season. The second decan of Aquarius marks the height of winter, at least symbolically speaking, in the northern hemisphere and now the snowdrops are here.

The Six of Swords in the Tarot deck is a card of recovery and onward progress. This can be read in terms of the natural seasons as the thawing, the passing of winter’s peak point, and now we are steering into spring.

The Gilded Tarot
See the toad in the rushes? The frogs and fishes are, right now, undergoing a alchemy of profound physiological changes, getting ready to spawn.
The light is coming back again, galloping faster it seems, by the day. Dark sacred night’…yes, and the night is dark. It is sacred. It brings rest and healing. But when the dark goes on too long, we start fighting back with the Promethean gift of fire and action.
We are HERE. And we overcame such odds just to be here, to get born as US and not someone else. Science suggests the statistical odds against you and me getting born as us and not someone else were 1 in 400 trillion. Yet here we are. Somehow WE burst through.
We must have had the need. We must have had our reasons. Mighty powerful ones.
Back soon.
Thank you for reading.












